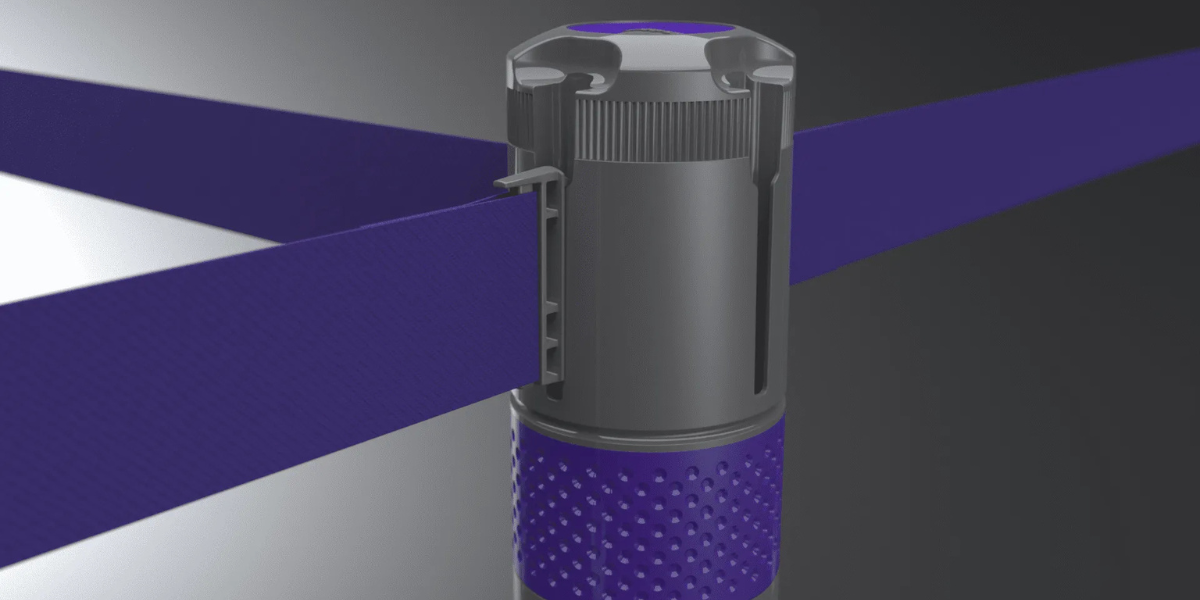
In the world of crowd control and public guidance, the evolution of retractable barrier systems marks a journey of innovation, design ingenuity, and technological advancements.
From their inception to the latest developments exemplified by one of 4D’s recent projects, the Skipper Q system. These tools have undergone significant transformations, becoming more than just functional devices; they've evolved into integral components of safety management with a keen eye on aesthetics and environmental responsibility.
This blog post delves into the technological advancements and design innovations that set the Skipper Q system apart from its predecessors and competitors, highlighting the slow retraction mechanism among its many forward-thinking features.
Retractable barrier systems made their debut as simple yet effective solutions for queue management and area cordoning. Initially, their design focused purely on functionality, with minimal attention to style or environmental impact.
Early models were often bulky, with a fast-retracting tape that could pose safety risks, such as snapback injuries, and were made from materials that paid little heed to sustainability.
As the demand for more sophisticated solutions grew, the industry saw a pivot towards integrating style with function. The introduction of the Skipper Q post and base system represents a pinnacle in this evolution.
Unlike its predecessors, Skipper Q marries sleek, modern design with unparalleled functionality, standing out not just for its appearance but for its innovative features that enhance user experience and safety.
Retractable barriers are no longer just practical tools; they're part of the venue’s aesthetic and brand identity. With a wide array of finishes and customisable options, barriers can now complement interior designs or corporate themes, making them a subtle yet integral part of the user experience. This evolution towards aesthetic integration has seen facilities achieving a more cohesive look, enhancing the overall ambiance and visitor perception.
For example, surveys indicate that venues with customised barriers see an approximate 20% increase in visitor satisfaction scores, underscoring the value of aesthetics in public space management.
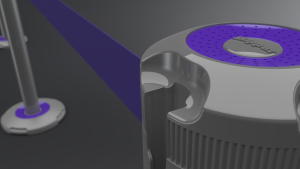
A pivotal advancement in retractable barrier technology is the introduction of slow retraction mechanisms. This feature stands as a testament to the industry's commitment to preventing the snapback incidents that were all too common with earlier models.
In practical terms, this innovation means that in high-traffic areas - be it bustling airports, vibrant shopping centres, or dynamic event venues. The risk of injuries from fast-retracting tapes is significantly minimised.
One of the hallmark advancements in the Skipper Q system is its slow retraction mechanism. This feature significantly reduces the risk of injuries that can occur when the barrier tape snaps back rapidly during retraction.
By engineering a controlled retraction speed, Skipper ensures a safer environment for users, mitigating potential accidents and enhancing the overall user interaction with the product.
The Benefits Are Clear:
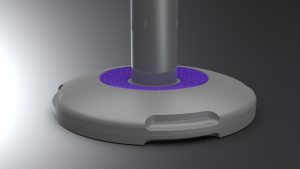
Gone are the days when a slight nudge could topple crowd control barriers. The introduction of weighted and stabilised bases has been a game-changer, enhancing the safety and reliability of these systems.
Modern barriers boast bases that can be filled with sand or water, significantly increasing their weight and stability. This advancement has led to a reduction in accidents related to barriers tipping over, contributing to safer environments in events, retail spaces, and airports worldwide.
Industry studies suggest that stabilised bases can increase a barrier's resistance to tipping by up to 75%, a testament to their effectiveness in crowded or outdoor settings.
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, the even retractable barriers need to update their use of materials and methods of production. Material innovation has propelled retractable barriers into the future. High-impact plastics, aluminium, and stainless steel are not just about longevity; they offer weather resistance and versatility.
This shift has not only extended the lifecycle of barriers, reducing the need for frequent replacements by as much as 50%, but also allowed for their use in diverse environments, from the sunny fields of Coachella to the rainy streets of Manchester.
Made from recycled materials and fully recyclable at the end of its life, Skipper Q addresses the environmental concerns that were often overlooked in earlier retractable barrier designs.
This commitment to sustainability not only enhances the product's appeal to eco-conscious buyers but also aligns with global efforts to reduce waste and promote recycling.
While specific, up-to-date statistics on injury reduction or sustainability impacts directly related to the Skipper Q system might not be readily available, industry studies have consistently shown that workplace and public space injuries from equipment can be significantly reduced with the adoption of safer, more user-friendly designs.
Furthermore, the push towards using recycled materials in manufacturing reflects a growing trend, with the recycling sector seeing a year-on-year increase in materials processing and reuse, emphasising the market's shift towards more sustainable product solutions.
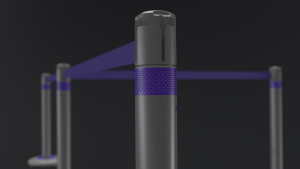
The complexity of modern crowd management calls for solutions that are as flexible as they are robust. The advent of modularity in barrier systems enables quick assembly, reconfiguration, and extension, catering to the dynamic needs of any event or space. This design philosophy ensures seamless integration of multiple units, creating a cohesive barrier system that can adapt on the fly.
If we think about the use of barriers at events, utilising modular barrier systems have reported up to a 30% reduction in setup and takedown times, highlighting the efficiency gains from this innovation.
As we navigate the complexities of public space management in today's world, the Skipper Q post and base system emerges not just as a tool, but as a solution that embodies the advancements and aspirations of the retractable barrier industry. It showcases a blend of innovation, safety, and sustainability, marking a significant leap from the rudimentary designs of the past.
For industry professionals looking to elevate their space management solutions, Skipper Q represents the pinnacle of what retractable barriers can achieve—setting a benchmark for future innovations in the field.
In conclusion, the evolution of retractable barrier systems, culminating in the development of the Skipper Q system, illustrates a journey towards smarter, safer, and more sustainable public guidance solutions.
As we look forward, the Skipper Q system offers a glimpse into a future where technology, design, and environmental consciousness converge to create products that not only serve practical purposes but also contribute to a safer, more aesthetically pleasing, and greener planet.